General questions
Do you have ideas and don’t know what to do with it? Contact us.
You give us your idea, we analyze it based on our own 3D printing experience and propose a project based on experience and all the possibilities of 3D printing and 3D modeling.
All work can be divided into 3 simple steps:
1) Idea analysis and project development, approval.
2) Creation of a 3D model and its completion.
3) 3D printing according to the required technology, processing, painting, varnishing.
Our experience and your ideas will make 3D printing easy and simple.
We need to share our ideas!
And to be more precise, it is necessary to formulate a technical task.
This is just a visual representation of the idea.
Answer the questions:
- meaning, purpose, what is it for?
- what functions and features are required?
- dimensions, color and quality of 3D printing
material quality for 3D printing
Anything that can be printed on a 3D printer.
Here are the basic ideas for 3D printing:
- instrument cases, various devices and useful little things
- children’s toys, figurines, decorative items, souvenirs
- molds for printing
prototypes of parts and mechanisms
vases, bottles
and much more
You can pay for the order on our website or we will send you an invoice by mail or messengers.
Delivery is carried out through transport companies throughout Europe
3D printing
3D printing is the process of creating a part from a material (plastic, resin, metal) from a digital 3D model. The method of creation varies greatly, but for example, FDM printing (the most popular method of printing) resembles squeezing toothpaste out of a tube. And so layer after layer of molten material is squeezed out, cools down and sticks to the already solidified material.
3D printer is a device that prints parts. Since there are so many ways of printing, there are a huge number of different 3D printers. But they all have common characteristics that you need to know when choosing a 3D printing method.
These are material, area, accuracy and layer height.
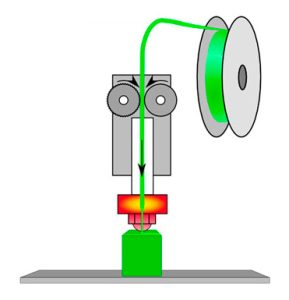
FDM (FFF) printing (thermoplastic) – 3D printing by layer-by-layer fusion. The heated nozzle receives a filament of plastic, the plastic melts and is pressed out of the nozzle. Solidifying it sticks to the table and already cooled plastic.
The material used is plastic with a melting point of 190 to 260 degrees centigrade. These are such materials as PET-G, PLA, ABS, Carbon, Neylon.
Pros of the method: ease of printing, the ability to print large parts and prevalence, cheapness and durability of materials. Minuses: relatively low melting point of materials, layering and low quality and detail of printing. Often requires machining of the resulting parts after printing.
FDM is used for prototyping, printing of various small things, housings, parts of mechanisms, gears and much more. It is the most popular and widespread method of 3D printing. FFF differs from FDM in that the quality of printing of the former is better due to the use of higher quality equipment.
SLA (DLP, LCD) printing (photopolymer resin) – printing using the property of resin to harden under the influence of laser or ultraviolet light. In a transparent bath poured photopolymer resin, in which the platform is lowered and illuminated by laser areas, after which the platform is raised and a new layer is again illuminated.
Pros: very high quality and detail, the possibility of printing completely transparent things.
Minuses: high cost of materials, their fragility, complexity of printing, smaller printing area. Does not require post-processing after printing.
It is used in jewellery, medicine and for printing souvenirs and decorative elements.
In addition, due to the use of ABS-Like, a durable photopolymer resin, it is possible to print durable and high quality parts.
CJP printing (gypsopolymer) – printing by gluing special powdered gypsum, after which a coloured pattern is applied to the outer surface. The gypsopolymer is poured into a tub, it is levelled and a special head glues and then colours the part, the unglued gypsum serves as a support for the part.
Pros: no supports, so the consumption of material is not more than the volume of the model, multicolour printing.
Minuses: high cost of equipment and material, fragility of the obtained products.
It is used in art and souvenir printing.
SLS printing (polyamide) – 3D printing by gluing polyamide powder by means of laser. A special bath is filled with powdered polyamide, after which the laser glues layer by layer. The unglued material acts as a support.
Advantages: no supports, so material consumption is minimised.
Disadvantages: high cost of equipment and material, graininess of the surface, necessity of post-processing of the surface.
It is mainly used for prototyping and printing of very strong parts.
Layer thickness (height)
In all types of 3D printing, the printer prints a layer, then the platform (head) is raised and a new layer is printed.
Layer thickness is the difference between the height of the new layer and the previous layer.
It is measured in mm or microns (1 micron equals 0.001 mm) and usually ranges from 0.05 mm to 0.3 mm.
The greater the layer thickness, the more layers are visible and the worse the detail of the part and rougher the 3D printing will be. SLA printers are capable of printing layer thicknesses up to 0.005 mm, while popular FDM printers can print up to 0.05 mm.
Layer thickness is a very important characteristic of printing, the quality of printing depends on it. But the smaller the layer thickness, the longer it takes to print a part and the more expensive the cost of printing.
Quite often very high print quality is not required or the part is geometrically simple and very good quality is not required,
In most cases, a 3D printing specialist can determine the required print quality and recommend optimal print settings.
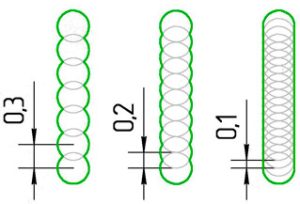
Filling density
Usually, in order to save material, the part is made hollow and to maintain the strength, partitions are made inside to give rigidity to the part.
The higher the density, the stronger the part. In most cases, 15-25% of the part filling is sufficient.
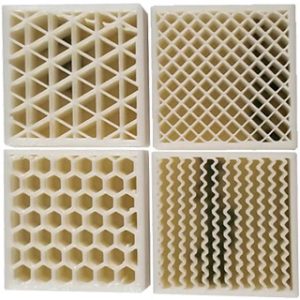
Wall thickness
In the case of hollow part printing, the wall thickness of the part is usually set from 0.8 mm. For strength it is increased up to 2-3 mm. In case of maximum strength, the part is made with 100% filling.
Supports. Angle and density of supports
During printing, parts of the pattern can overhang and be deformed by gravity. To prevent this from happening, supports are printed along with the part, most often made of the same material as the part itself.
The overhanging angle of the part, at which the supports are built and their density depends on the material and geometry of the shape. For example, ABS plastic, due to its increased fluidity when heated, requires denser supports and a lower overhang angle. When printing with PLA plastic, it solidifies on the fly and may not need any support at all.


When printing with a twin nozzle printer, another material can be used as a backing material that dissolves after printing.
For example, for PLA plastic, PVA (solid PVA glue) can be used as backing material, which is dissolved in water after printing.
For ABS laminates, HIPS can be used as support material, which is dissolved in Limonene.

Print speed
The speed at which the printer print head moves, measured in mm/s.
The higher the speed, the worse the print quality, but the faster the printing. Typical print speeds are 45-65 mm/s, but it is better for a specialist to determine the required print speed, because for example Flex printing requires a print speed of no more than 25 mm/s, while PLA allows 60-70 mm/s.
Default 3D printing characteristics (settings)
Settings of the main printing parameters that significantly affect material consumption and print quality. The cost of printing is calculated based on the default settings. If printing with other settings is required, we will or should notify you.
Layer thickness (height) – 0.25 mm.
Wall thickness – 0.8 mm.
Fill density – 15% .
Printing speed – 65mm/s
Support density – 15%
Overhanging angle of supports – 75 degrees
Position on the printing table – at the operator’s discretion. The print operator chooses the position of the part himself based on minimisation of plastic consumption, maximum possible quality of external surfaces, minimisation of supports and taking into account his own experience.
You can automatically calculate the cost of 3D printing on the 3D calculator page.
The price on the website is per 1 gram of material. The actual cost and discounts are shown on our promotions page
The practice of calculating the cost of printing:
The volume of material used is in most cases less than the volume of the 3D model, as we make the part hollow with default filling to save money. However, if maximum strength or a transparent part is required, we make with 100% fill.
FDM printing is printing by layer-by-layer fusion. Material (in most cases thermoplastic with melting point 190-260 degrees) in the form of filament goes into the heated nozzle, there it is melted and comes out in a heated state from the nozzle, and solidifying sticks to the previous layers and to the table. Reminds me of squeezing toothpaste out of a tube. After one layer, the printer head rises to the height of the layer and prints the next layer.
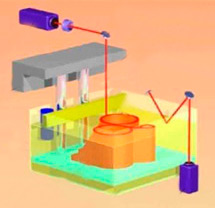
How does SLA printing with photopolymer resin work?
The laser beam is guided by a system of mirrors into a bath of liquid photopolymer resin, which is cured by light. The platform is then raised and the laser beam passes through the next layer.
Shrinkage
The most common problem. During printing the material shrinks as it cools down, reducing in size by up to 3%. For example, on large parts (from 10 cm) the edges tear off the table and the geometry of the part changes.
Shrinkage depends on the material and filling. Some materials such as ABS, Neylon, PC have strong shrinkage, and other materials (PLA, PET-G, photopolymer resin) have low shrinkage.
Our experts determine the best material for printing and recommend it.
Defects after removal of supports
Supports are often required for printing. Since they are printed from the same material as the part, they must be removed. In addition, an uneven, rough surface is created where the supports are attached.
Specialists try to position the part in such a way that the supports are not on the front side but on the back side (inner surface), but it is still necessary to remove the supports and treat the surface after removal.
Layering
In FDM printing, especially with layer thicknesses of 0 0.25 mm and above, due to the nature of the print, layers (layering) are visually visible.
To reduce layering and to make the surface smooth it is possible to reduce it mechanically (grinding) or chemically (solvent treatment).
Poor quality printing of small elements
Not all printers can print small details or elements of the model (up to 5 mm) correctly and qualitatively. In this case it is better to print with photopolymer resin.
The part is one-colour after printing and often needs to be reworked.
Removing supports
After printing, it is often necessary to remove supports.
Since special tools and expertise are required to remove them, this service is charged separately. In case it requires little time, we remove them free of charge.
Creating a smooth and glossy surface
Very often after printing it is necessary to remove layering and correct rough surfaces after removing supports. This is done by mechanical treatment (sanding), puttying and chemical treatment to create a glossy surface. The service is charged separately and is calculated individually.
Priming and painting
As the printing is done in one colour, it is necessary to prime and paint the part. Our professional painters do the painting inexpensively. The service is charged separately and is calculated individually.
Popular materials for FDM printing:
PET-G – plastic with good interlayer adhesion, has low shrinkage, used for printing housings, gears, useful little things, can be used for printing utensils
PLA – a completely environmentally friendly plastic, made from corn, excellent for printing souvenirs, figurines, children’s toys.
ABS – a durable plastic with a large temperature range of operation, used for printing gears, housings, automotive elements.
Carbon – super strong carbon with the addition of carbon fibre. Excellent for printing highly loaded parts of mechanisms
Popular types of photopolymer resin:
Basic Photopolymer Resin. Great for inexpensive quality printing of figurines, precision parts
ABS-Like. Reinforced photopolymer resin. If you need precision, quality and durability, this material is the ideal choice
For other 3D printing materials and to see the characteristics of materials, please visit the 3D printing material selection page.
